Chemical Structure
- Home
- Chemical Structure
Chemical Structure of Alginates
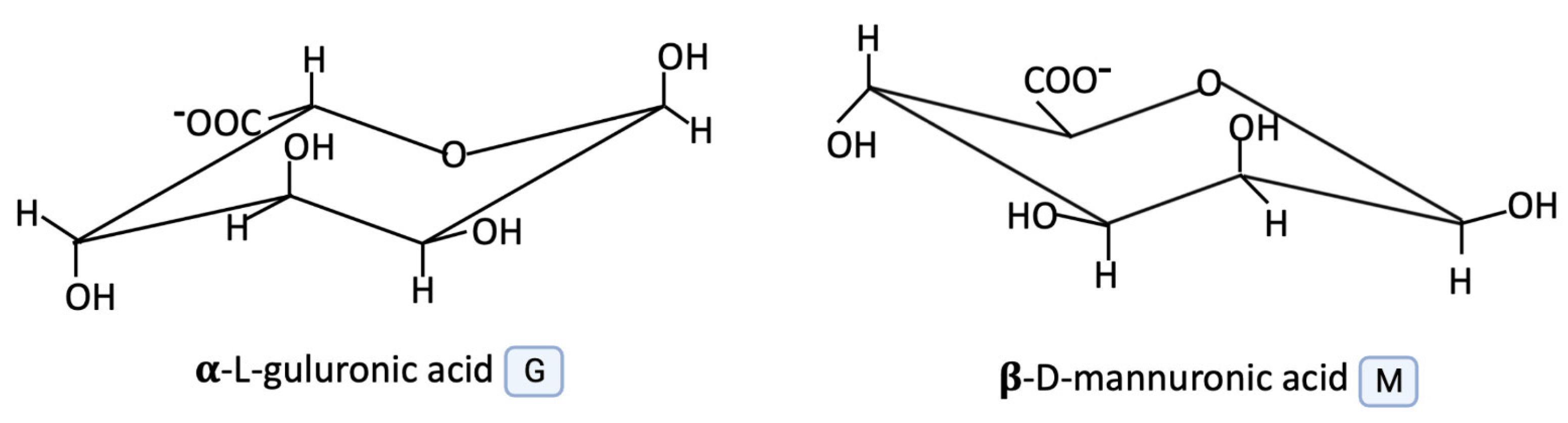
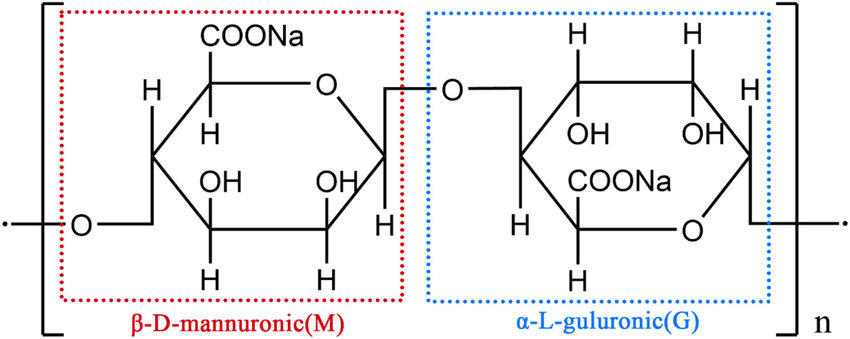
Alginates are naturally occurring polysaccharides derived from brown seaweed. They are composed of linear copolymers of two uronic acids:
- β-D-mannuronic acid (M)
- α-L-guluronic acid (G)
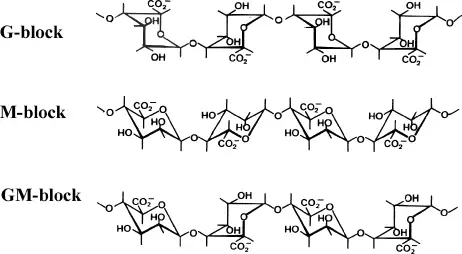
These acids form homopolymeric (M-blocks, G-blocks) and heteropolymeric (MG-blocks) sequences in the alginate chain. The general structure is represented as: [-Mn−Gm−] Where M and G units are linked via (1→4) glycosidic bonds. The molecular structure and block composition influence the gel-forming properties of alginates, which are widely used in pharmaceuticals, food, and biotechnology.
Key Properties of Alginates:
- Water-soluble in sodium salt form
- Gelation occurs in the presence of divalent cations (e.g., Ca²⁺)
- Forms thermally stable gels
- Biodegradable and biocompatible